Abbreviations
V : Volts
A : Amperes
W : Watts
mA : miliAmperes
VA : Volt Amperes
VAC : Volts AC
VDC : Volts DC
DC : Direct Current
AC : Alternating Current
Components
Conductors are materials through which electrical current moves freely.
Insulators are materials which prevent the flow of electricity.
Resistors resist, but do not totally block, the flow of electricity. They are used to control the flow of current. Current can move either way through a resistor, so it doesn’t matter which way they’re connected in a circuit. They are symbolized like this:

Capacitors store up electricity while current is flowing into them, then release the energy when the incoming current is removed. Sometimes they are polarized, meaning current can only flow through them in a specific direction, and sometimes they are not. If a capacitor is polarized, it will be marked as such on the diagram. Don’t wire a polarized capacitor backwards; it might explode.
Capacitors are symbolized like this:

Diodes permit the flow of electricity in one direction, and block it in the other direction. Because of this, they can only be placed in a circuit in one direction. They are symbolized like this:

Light-Emitting Diodes (LED’s) are special types of diodes which emit light when current flows through them. They are symbolized like this:
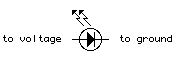
There are many other types of components which you’ll come across:
- switches control the flow of current through a junction in a circuit:
- transistors and relays are switching devices:

- thermistors change resistance in reaction to varying temperature;
- photoresistors change resistance in reaction to varying light;
- flex sensors change resistance in reaction to being bent or flexed;
- piezoelectric devices create a varying voltage in reaction to slight changes in pressure.